Why Should You Know Ipconfig /displaydns
The ipconfig (brusk for IP Configuration) is a bones, yet pop, Windows network command-line utility used to display the TCP/IP network configuration of a computer. If you lot are familiar with Linux, this tool is similiar to ifconfig. This tool is often used for troubleshooting network connectivity issues. With ipconfig, you lot tin identify the types of network adapaters on your figurer, the computer's IP address, the IP addresses of the DNS (Domain Name Organisation) servers being used, and much more.
These commands shown here are tested on a comptuer with Windows 10 just most will work in other versions of Windows besides.
Tabular array of Content
- Overview
- How to Launch Command Prompt
- Ipconfig Syntax
- Ipconfig Parameters
- Example Usage
- ipconfig - Retrieves Basic TCP/IP Network Information (IP, subnet mask, gateway)
- ipconfig /all - Retrieves All TCP/IP Network Information (MAC address, adapter description, DHCP details)
- ipconfig /release - Releases the IPv4 Accost of All Network Adapters
- ipconfig /release6 - Releases the IPv6 Address of All Network Adapters
- ipconfig /release <adapter> - Releases the IP Address of a Specific Network Adapter
- ipconfig /renew - Go a New IPv4 Address for All Network Adapters
- ipconfig /renew6 - Go a New IPv6 Address for All Network Adapters
- ipconfig /renew <adapter> - Get a New IPv4 Address for a Specific Network Adapter
- ipconfig /displaydns - View DNS Cache
- ipconfig /flushdns - Purge DNS Enshroud
- ipconfig /all | findstr /v 00-00-00 | findstr Physical - Display MAC Address of But Physical Connected Network Adapters
- Other Usages and Getting Help
- Tips
- Redirect Output to Text File
- Recommended Reading
- Summary
Overview
The ipconfig is a Windows command-line utility used often to troubleshooting figurer network issues. If you are a Linux user, this utility is like to ifconfig. This is often used to decide the local IP address, subnet mask, the gateway address, and other network configuration of a computer. Additionally, this tool is used to refresh DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) and DNS (Domain Name Organisation) settings
While most of the data provided past the ipconfig command-line utility can be found via a more user-friendly graphical interface, sometimes that interface may non be bachelor and command prompt is your only available option. If you are a assistance desk technician or a network professional, information technology is recommended that you understand the command-line method of retrieving a estimator's network configuration, and it some cases, performing network functions.
How to Open up Control Prompt
To use this utility, you volition need to launch the Command Prompt window. The 3 mutual means to launch the Control Prompt window are:
- Search for
cmdusing the built-in Windows search tool. - Correct-click on the Start icon and select Command Prompt.
- Printing the keyboard combination WinKey + R , then type
cmdat the Run window that appears.
Ipconfig Syntax
ipconfig [/allcompartments] [/all] [/renew [<Adapter>]] [/release [<Adapter>]] [/renew6[<Adapter>]] [/release6 [<Adapter>]] [/flushdns] [/displaydns] [/registerdns] [/showclassid <Adapter>] [/setclassid <Adapter> [<ClassID>]]>
Ipconfig Parameters
| Parameter | Clarification |
|---|---|
| /all | Display the full TCP/IP configuration information for all network adapters. |
| /release | Release the IPv4 accost for the specified adapter. |
| /release6 | Release the IPv6 address for the specified adapter. |
| /renew | Renew the IPv4 address for the specified adapter. |
| /renew6 | Renew the IPv6 address for the specified adapter. |
| /flushdns | Purges the DNS Resolver enshroud. |
| /registerdns | Refreshes all DHCP leases and re-registers DNS names. |
| /displaydns | Display the contents of the DNS Resolver Cache. |
| /showclassid | Displays all the DHCP class IDs allowed for adapter. |
| /setclassid | Modifies the DHCP class ID. |
| /showclassid6 | Displays all the IPv6 DHCP grade IDs allowed for adapter. |
| /setclassid6 | Modifies the IPv6 DHCP class ID. |
| /? | Displays help information. |
Instance Usage
There are a variety of switches (sub commands) bachelor with the ipconfig utility that will either display certain data or perform certain network functions. At the most basic, the ipconfig displays a figurer'due south IP accost, subnet mask and the default gateway (which is typically the IP address of your router or network firewall).
ipconfig - Call up Basic TCP/IP Network Information
To go bones network information from your calculator, type the post-obit in the command window and so press Enter: ipconfig
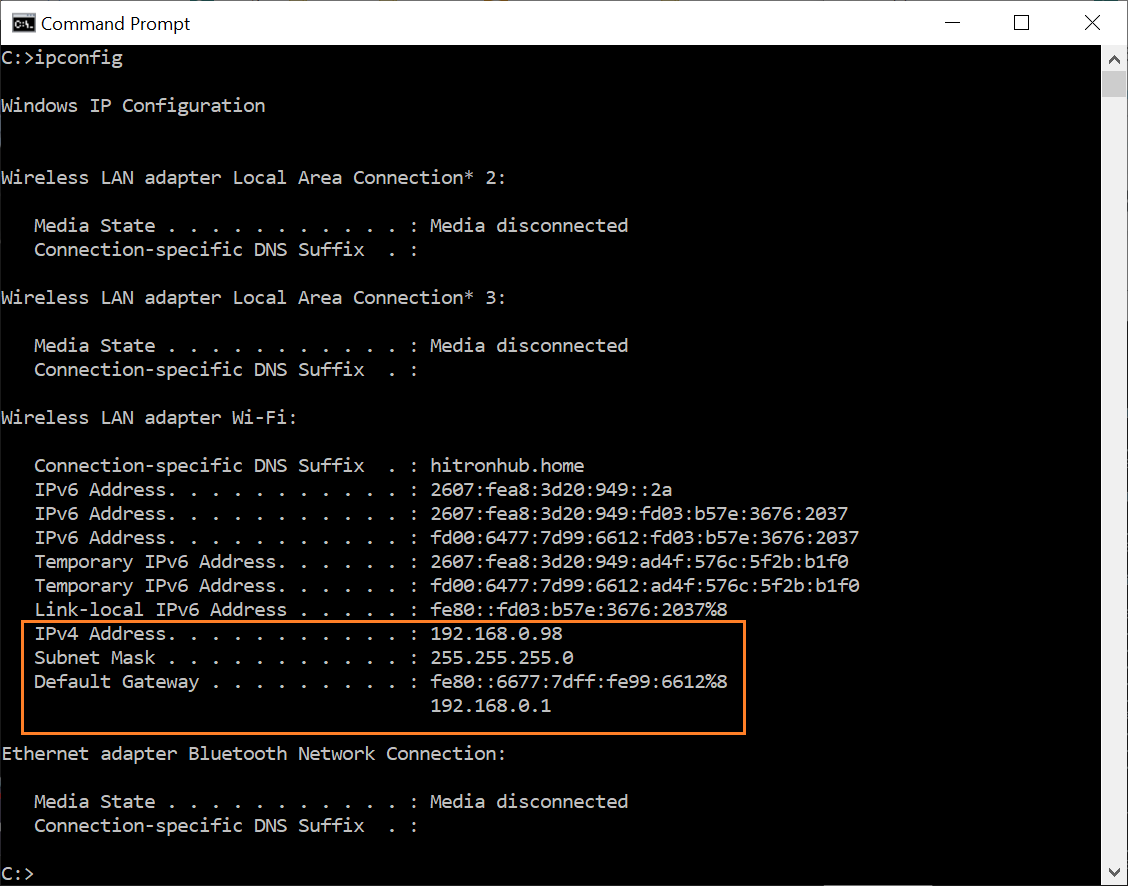
The screenshot example beneath is the ipconfig output of a particular computer. The output of your ipconfig event will differ depending on your network setup and the type of network adapters installed on your computer. In our screenshot example, information technology shows the following basic networking data nigh the figurer from which ipconfig was ran.
- IPv4 address: 192.168.0.98
- Network subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
- Default Gateway: 192.168.0.1
Delight note that unless your computer is connected directly to the Net (this is rare), the IP address reported past ipconfig will be your local network IP, not your public external IP address.
While other network details can be retrieved by the ipconfig utility, for most network troubleshooting, this is what is typically needed.
ipconfig /all - Retrieve All TCP/IP Network Information
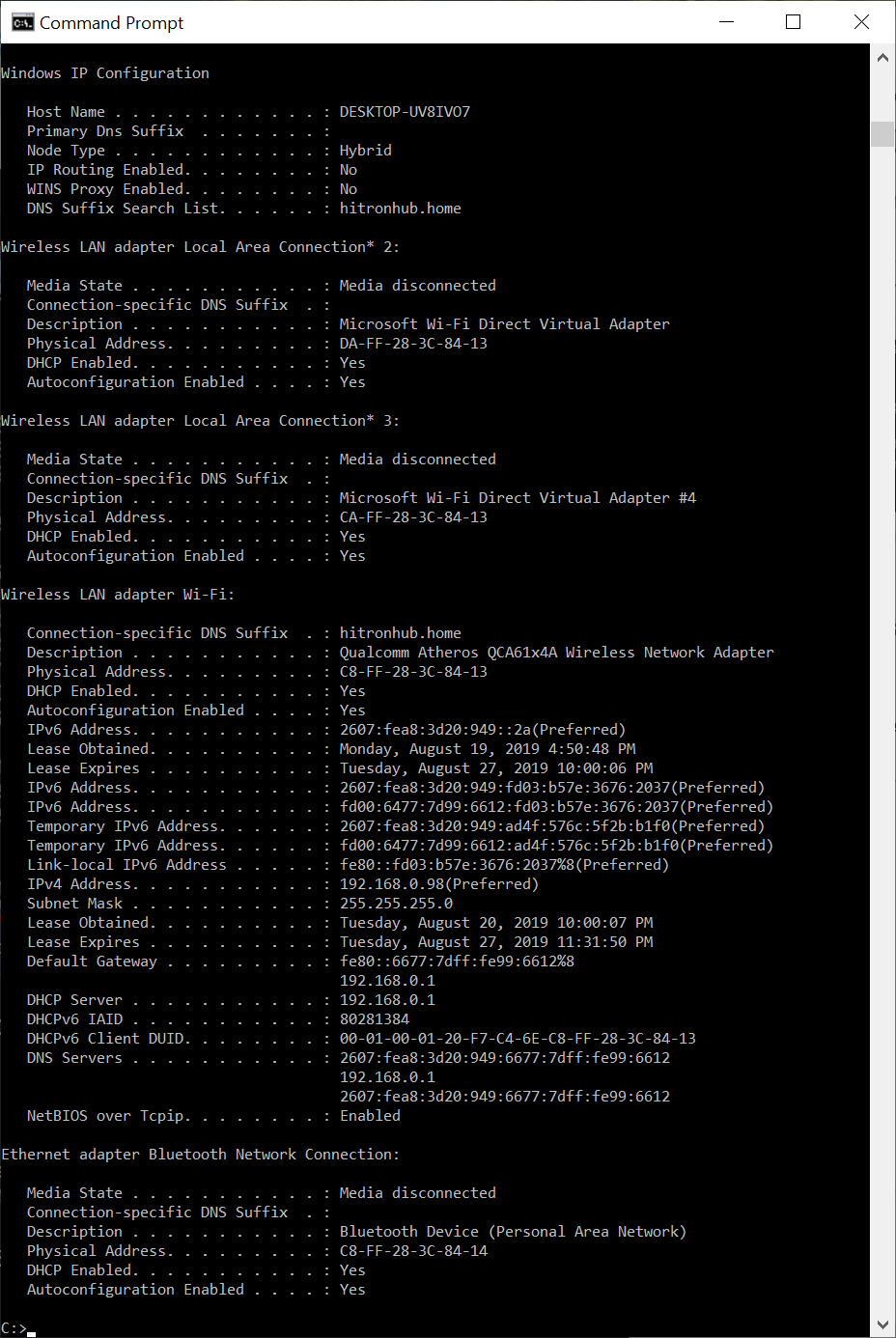
Another useful switch with ipconfig is to take it report all TCP/IP network details for all network adapters on a computer. This is accomplished by using the /all switch. This switch provides you with the aforementioned basic information as ipconfig described above, but with a lot more item. To retrieve all network information about your reckoner, blazon the following in the command window then press Enter: ipconfig /all
This volition prove a detailed report of various network details for the computer. Again, your report will differ depending on your network setup and the network adapters installed on your computer. This study includes information such as:
- Brand and model of your network adapter(southward)
- Physical accost (also known equally the MAC address or hardware accost) of your adapter(s)
- Whether your IP address is leased (i.e., DHCP issued or statically assigned)
- If IP accost is leased, what the lease expiration and the DHCP that leased it
- DNS servers
As you can come across, ipconfig /all provides you lot with a plethora of details about your computer network setup.
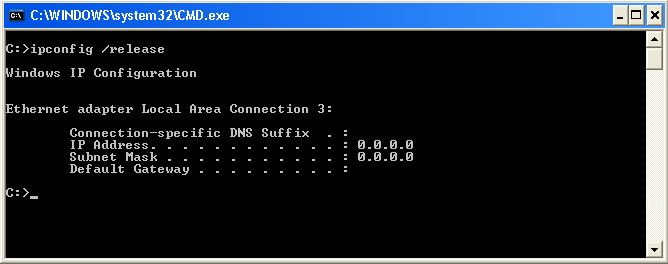
ipconfig /release - Releases the IPv4 Address of All Network Adapters
The /release switch volition cause ipconfig to go through the network adapters yous have and drop the dynamically issued IPv4 accost by sending a DHCPRELEASE message to the DHCP server. For the majority of the fourth dimension, y'all would follow this control with ipconfig /renew (described below) will cause your network adapters to reach out to your DHCP server for an IP accost (it can be a new IP accost or the same IP you had prior to when you performed the /release control). For well-nigh, executing this command does not have adverse effect on your figurer.
To release your IP address from your reckoner, blazon the following in the command window then press Enter: ipconfig /release
Note, if you have a statically assigned (manually assigned) IP address, this command will not release information technology. See example ipconfig /renew for related information.
ipconfig /release6 - Releases the IPv6 Address of All Network Adapters
The command is like to ipconfig /release except it renews the IPv6 accost on the adapters.
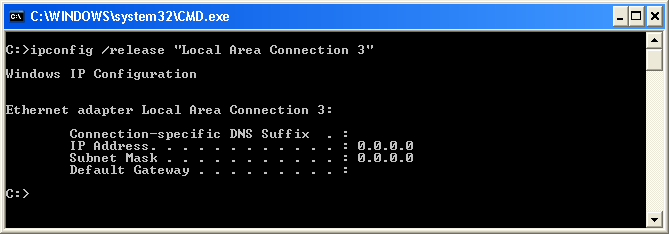
ipconfig /release <adapter> - Releases the IPv4 Address for a Specific Network Adapters
The /release <adapter> switch will crusade ipconfig to drop the dynamically issued IPv4 address by sending a DHCPRELEASE message to the DHCP server for a specific network adapter.
To release the IP address for a specific network adapter on your computer named "Local Area Connection iii", type the following in the command window and then printing Enter: ipconfig /release "Local Area Connexion 3"
Notation, if you have a statically assigned (manually assigned) IP address, this command will not release information technology. See example for ipconfig /renew for related information.
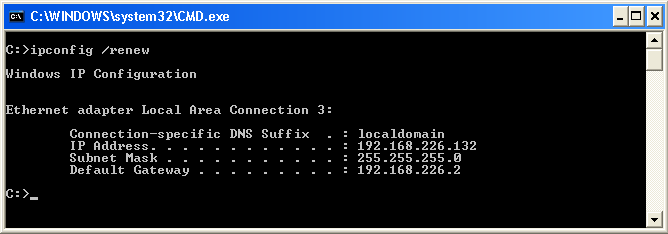
ipconfig /renew - Get a New IPv4 Accost for All Network Adapters
The ipconfig /renew will cause your reckoner to accomplish out to your DHCP server for an IPv4 address if it doesn't already accept one or renews an existing one for all network adapters. Depending on how your DHCP server is configured or the puddle of available addresses, the IP address you will receive can exist one you had previously or information technology tin can be a new IP address. Once you execute this control, it volition typically take just seconds for a DHCP to assign your computer with an IP address. In the illustration below, the IP accost assigned to this computer is 192.168.226.132.
To renew the IP address of your computer, type the following in the control window then printing Enter: ipconfig /renew
Meet instance for ipconfig /release for related information.
ipconfig /renew6 - Get a New IPv6 Address for All Network Adapters
The command is similar to ipconfig /renew except information technology renews the IPv6 accost on the adapters.
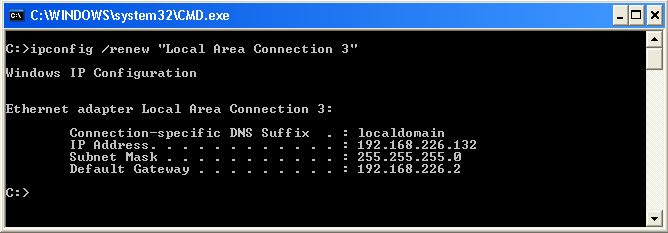
ipconfig /renew <adapter> - Go a New IPv4 Address For a Specific Network Adapter
The ipconfig /renew <adapter> volition cause your computer to reach out to your DHCP server for an IPv4 address if it doesn't already accept one or renews an existing one for a specific network adapter. Depending on how your DHCP server is configured or the pool of available addresses, the IP address yous will receive tin be one you had previously or information technology tin exist a new IP address. Once you execute this control, it will typically take just seconds for a DHCP to assign your calculator with an IP address. In the illustration below, the IP accost assigned to the network adapter named "Local Area Connection 3" is 192.168.226.132.
To renew the IP accost for a network adapter on your computer named "Local Expanse Connectedness 3", blazon the post-obit in the command window and then press Enter: ipconfig /renew "Local Area Connectedness 3". To notice out the name(south) of the network adapters on your computer, blazon the following in the command window then press Enter: ipconfig
See example for ipconfig /release for related data.
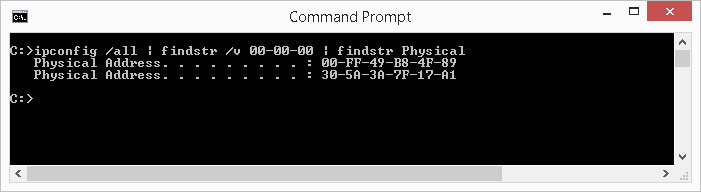
ipconfig /all | findstr /v 00-00-00 | findstr Concrete - Display MAC Address of Just Physical Continued Network Adapters
The ipconfig utility, with the /all switch, is often used to find the MAC address (the half-dozen-byte 'burned-in' physical/hardware address) of network adapters. While this does the job, the output shows a plethora of information as mentioned higher up. If yous have multiple adapters, the output can be lengthy making it cumbersome to find what you are looking for.
The Windows findstr utility is used to search for patterns of text. By feeding the output of ipconfig /all into findstr, nosotros tin can significantly reduce the clutter and have the output show only the MAC accost of physical network adapters. To accomplish this, type the following in the control window so press Enter:
ipconfig /all | findstr /five 00-00-00 | findstr Physical
This control is actually a series of iii commands, namely:
-
ipconfig /all -
findstr /5 00-00-00 -
findstr Physical
The vertical bar (|), more commonly referred to as the pipage, is a 'command' that takes the output from the left side of the pipe and feeds it equally input to the command on the correct, bypassing the computer screen.
As the above command shows, the output of ipconfig /all is funneled into the command findstr /v 00-00-00 every bit its input. The findstr with the /5 switch will look for lines of text in the output of ipconfig /all that does non contain 00-00-00. What this does is exclude any network adapters that are disabled or not continued. These network adapters will have MAC address that starts with 00-00-00.
The event from the outset findstr volition notwithstanding comprise a lot of information that we can further filter out, such as DHCP lease information. To further reduce ataxia to ultimately end upward with an output that lists simply MAC address of physical adapters, we will demand to funneled the output of the first findstr into a second findstr command. This second findster will filter out every line of text except those that has the give-and-take Concrete.
This series of commands produce an output that is curtailed to show only the MAC address of connected network adapters. As the illustration below shows, this is a much more easier report to read every bit oppose to using just using ipconfig /all.
ipconfig /displaydns - View DNS Cache
When you visit a website using it'due south domain name (e.g., www.meridianoutpost.com), your computer will need to know the IP address for that website in social club for information technology to find it the server hosting it on the Cyberspace. The process of identifying the IP accost is called DNS lookup (coordinating to looking up a number in a phone volume). Once your calculator learns the associated IP address for the website you lot desire to visit, it volition cache it (shop it) on your computer. The purpose of caching information technology is to improve performance by not having your computer perform a DNS lookup each time y'all access a web page on the website.
This command will listing all the currently buried IP addresses on your calculator (likewise referred to as the DNS resolver cache). If you've accessed a lot of websites since turning on your calculator, this list can be very lengthy. The illustration below shows just a few entries out of many for a particular computer. If you simply turned on our computer and have not access websites or servers on the network on the Internet, then you list volition only show a "localhost" setting in your local hosts file.
To display buried DNS entries on your calculator, type the post-obit in the command window and so press Enter: ipconfig /displaydns
This command is typically used to troubleshoot specific DNS lookup issues. Come across example for ipconfig /flushdns for related data.
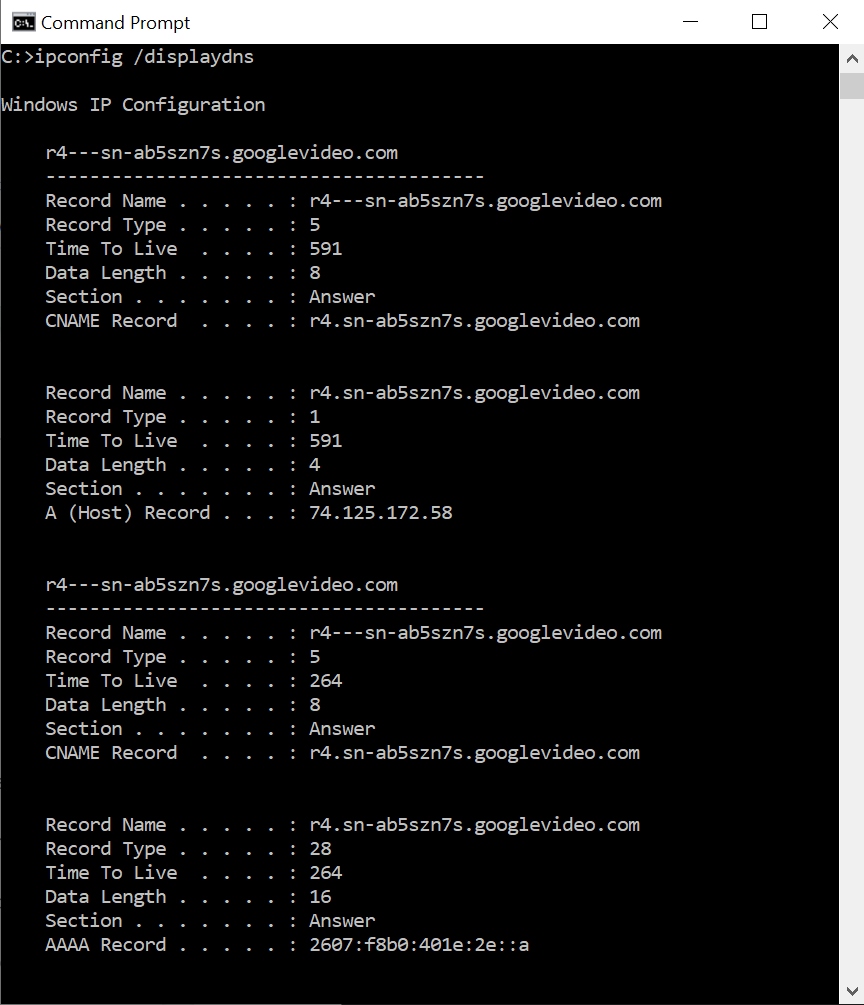
The data displayed on the listing include:
- Record Name: the name of the website or server that a DNS lookup was performed on
- Record Type:
- 1 = A
- 2 = NS (indicates the entry is a name server)
- 5 = CNAME (stands for approved name and is a type of tape that maps an alias proper name to a true domain name)
- xv = MX (indicates the entry is an email server)
- Time to Alive: the fourth dimension (in seconds) earlier this cache entry expires (tin can exist every bit short as a few minutes to a few days)
- Data Length: the length (in bytes)
- 8 Bytes = IPv4 address
- sixteen Bytes = IPv6 address
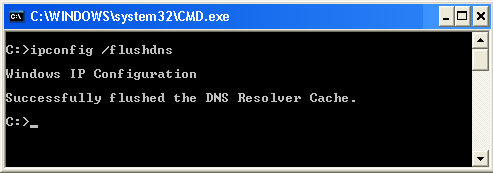
ipconfig /flushdns - Purge DNS Cache
This command will purge the cached DNS entries on your computer. Yous would typically do this to troubleshoot DNS related problems. An instance of this is when y'all try to access a website but you run into an fault message stating the website is not institute. For about people, executing this command does not have agin effect on your estimator. See instance for ipconfig /displaydns for related information.
To delete all the cached DNS entries on your computer, blazon the post-obit in the command window then printing Enter: ipconfig /flushdns
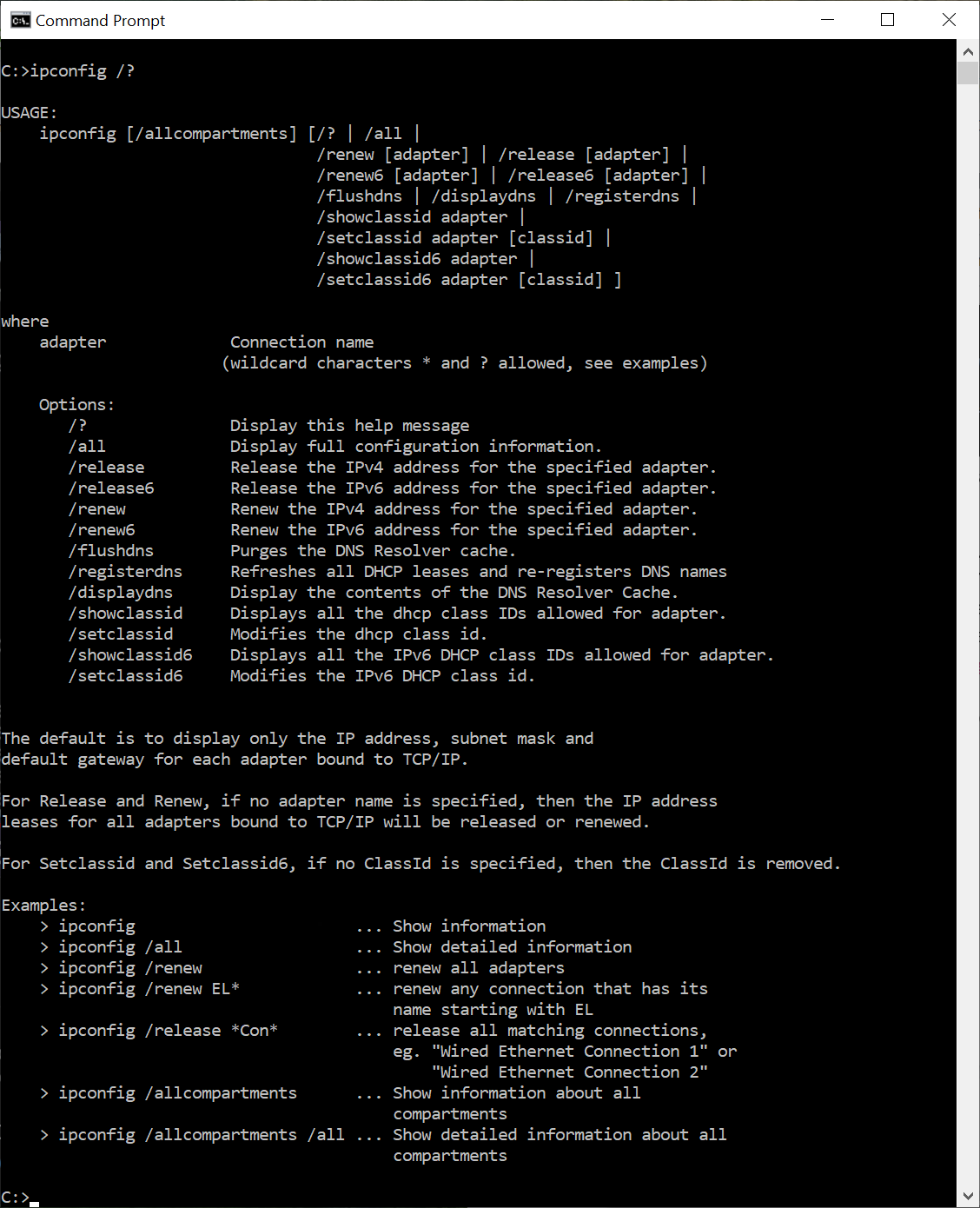
Other Usages and Getting Aid
The example usage described in the commodity shows only some of the functions available with ipconfig. To get a listing of the available switches, type the following in the command window so printing Enter: ipconfig /?
Tips
Redirect Output to Text File
- Instead of displaying the results on the screen, y'all can have the results saved automatically to a text file on your computer. To practise this, merely utilise the ">" symbol followed past the binder path and file proper noun of your pick. For example, to redirect the output of ipconfig /renew, type the post-obit in the command window then press Enter:
ipconfig /renew > c:\temp\ipconfig-results.txtThis will create a file named ipconfig-results.txt in the binder path c:\temp that will have your upshot. You can then open this file with any text editor, such every bit Notepad on a Windows computer, as illustrated beneath.
Recommended Reading
Improve confidence and chore operation
Ameliorate productivity and efficiency
Learn more,
earn more
Life-long
investment
To learn more about this topic, we are providing you with recommendations to assistance you further your knowledge. These are our affiliate links to Amazon where you can purchase them and too explore a multifariousness of other relevant books.
Summary
The ipconfig utility tin can provide a wealth of information for troubleshooting network bug. This utility is a valuable resource for computers that obtains an IP address automatically. If you lot are helpdesk technician, network administrator, or system administrator, this is a nifty utlity to become familiar with.
Why Should You Know Ipconfig /displaydns
Source: https://www.meridianoutpost.com/resources/articles/command-line/ipconfig.php
0 Response to "Why Should You Know Ipconfig /displaydns"
Post a Comment